This flowchart outlines a Backflush in Production process, representing a sample best practice approach commonly found in ie. automotive component manufacturing and similar industries utilizing SAP ERP systems for production planning. It details a streamlined method for production confirmation and material consumption, especially beneficial in high-volume, repetitive manufacturing (REM) scenarios typical of automotive parts production. This process is designed to ensure accurate inventory management and efficient cost accounting in SAP.
What is Backflush Process in SAP?: In repetitive manufacturing environments, particularly in industries like automotive component production, Backflushing is a method used to simplify and automate production confirmation and material consumption postings in an ERP system. Instead of manually issuing materials to production orders beforehand, the system automatically records the consumption of raw materials and posts the goods receipt of finished or semi-finished goods directly upon confirming the completed production quantity. This streamlined approach minimizes manual transactions, provides real-time inventory updates, and is well-suited for high-volume, consistent production processes common in automotive component manufacturing.
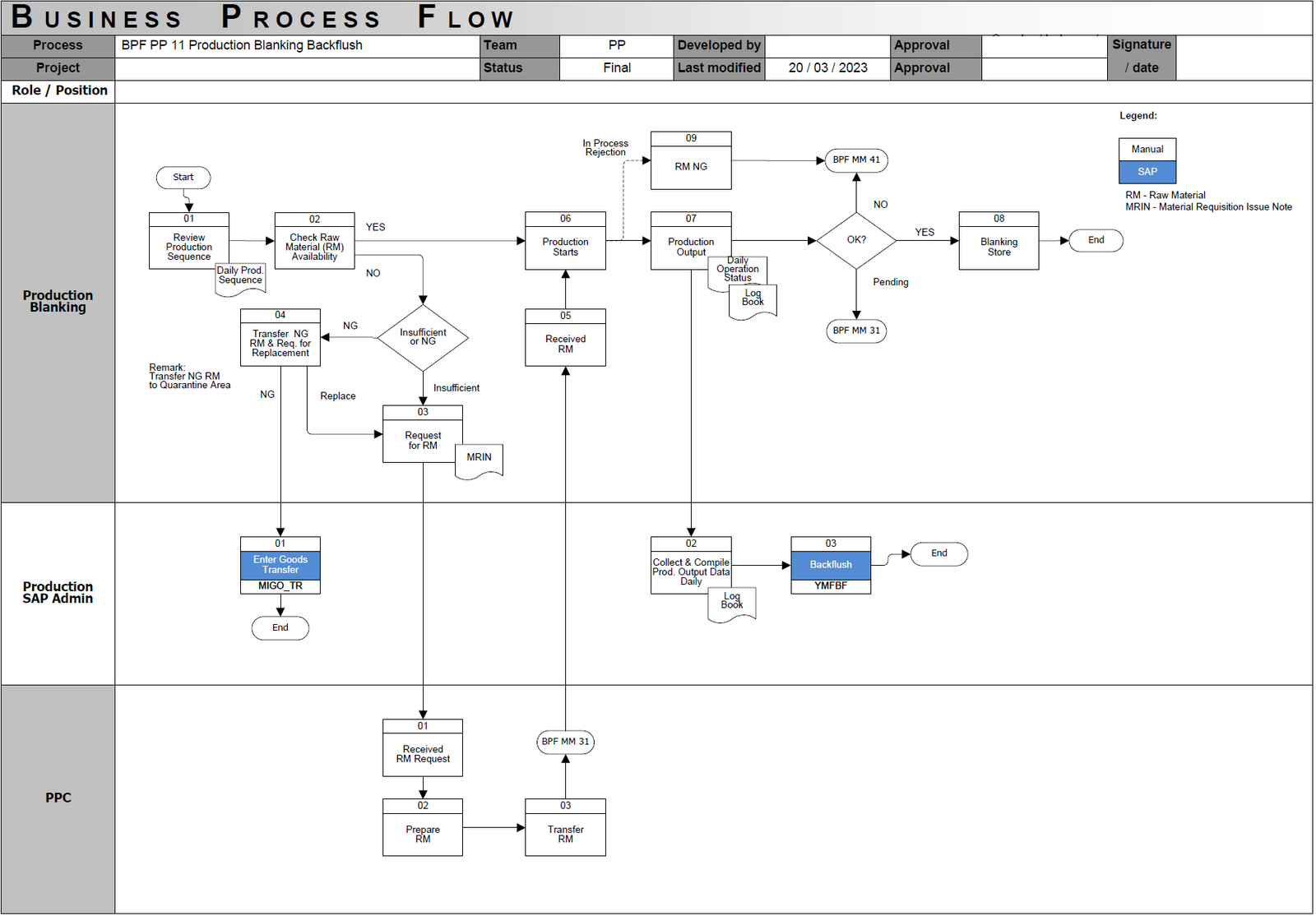
Process Steps for Backflush in Production Process in SAP PP:
A. Production Start and Material Availability Management:
- Review Production Schedule: The production team begins by reviewing the daily or shift production schedule to understand planned production targets and sequences.
- Verify Raw Material Availability: Before initiating production runs, it’s crucial to verify the immediate availability of necessary raw materials at the production area. This step ensures that production can proceed without delays due to material shortages or quality issues.
- Raw Material Request (Triggered if Needed): Should raw materials be unavailable at the production line (due to insufficient quantity or quality non-conformance), a formal request for raw materials is generated. This may involve creating a material requisition to prompt the warehouse to supply the needed materials.
- Raw Material Preparation and Staging: The materials planning or warehouse personnel respond to the raw material request by preparing and picking the required materials from storage. These materials are then moved and staged at the designated production area, ready for use.
- Goods Transfer Transaction (SAP System Update): Upon physical staging of the raw materials at the production line, a goods movement transaction is entered in the SAP system (using a transaction like MIGO_TR in SAP). This step documents the material transfer, updates inventory records to reflect materials issued to production, and ensures accurate tracking of material movement.
B. Production Execution and Automated Confirmation:
- Production Commences: With raw materials staged and verified, the manufacturing or production operation begins.
- Daily Production Data Collection: Throughout the production process, operators meticulously collect and compile daily production data. This includes quantities produced, any rejected parts, downtime, and other relevant operational information, typically documented in a daily log or operational status record.
- Production Output Validation and Quality Check: Production output is tallied and undergoes quality inspection. If the produced components meet quality standards (“Output OK? YES”), the process advances to the final confirmation stage. If any output is rejected during in-process checks due to quality issues (“In-Process Rejection”), these non-conforming parts are segregated. Rejected materials are then handled through a defined non-conformance process, potentially involving transfer to a quarantine area or scrap disposal, and may initiate requests for replacement raw materials to maintain planned production volumes.
- Production Backflush Execution (SAP System – Automated Confirmation): At defined intervals (e.g., end of shift, completion of a production run), production output is confirmed in the SAP system by executing a backflush transaction (using MFBF Tcode). This single transaction serves to confirm the quantity of finished goods produced and automatically triggers two key SAP postings:
- 1) Goods Receipt for the finished or semi-finished products, increasing their stock levels in inventory, and
- 2) Goods Issue (Backflush) for the raw materials consumed in production, automatically reducing raw material inventory based on the defined Bill of Materials for the product.
- Goods Receipt to Storage: After the successful SAP backflush, the system automatically posts the goods receipt, and the manufactured components are physically moved to their designated storage location (e.g., a finished goods store or intermediate storage), reflecting the updated inventory of produced items.
- Process Completion: The Production Backflush process concludes with the accurate and automated recording of production output and associated material consumption, ensuring up-to-date inventory levels and cost data in the SAP system with minimal manual data entry.
C. Management of Non-Conforming Raw Materials:
- Handling Rejected Raw Materials and Replenishment: When raw materials are identified as non-conforming (“Rejected Raw Material”), these materials are physically moved to a designated quarantine zone or scrap area. Depending on the production plan and material requirements, a process to request and procure replacement raw materials may be initiated to compensate for the rejected stock and avoid production disruptions.
- Non-Conforming Material Inventory Adjustments: The movement of rejected raw materials is also documented in the SAP system, likely involving inventory adjustments or scrap postings. This step maintains inventory accuracy by reflecting the removal of non-conforming materials from usable stock and ensures proper accounting for material losses or scrap.
La información en esta página es excelente, se entiende y explica muy bien. Gracis