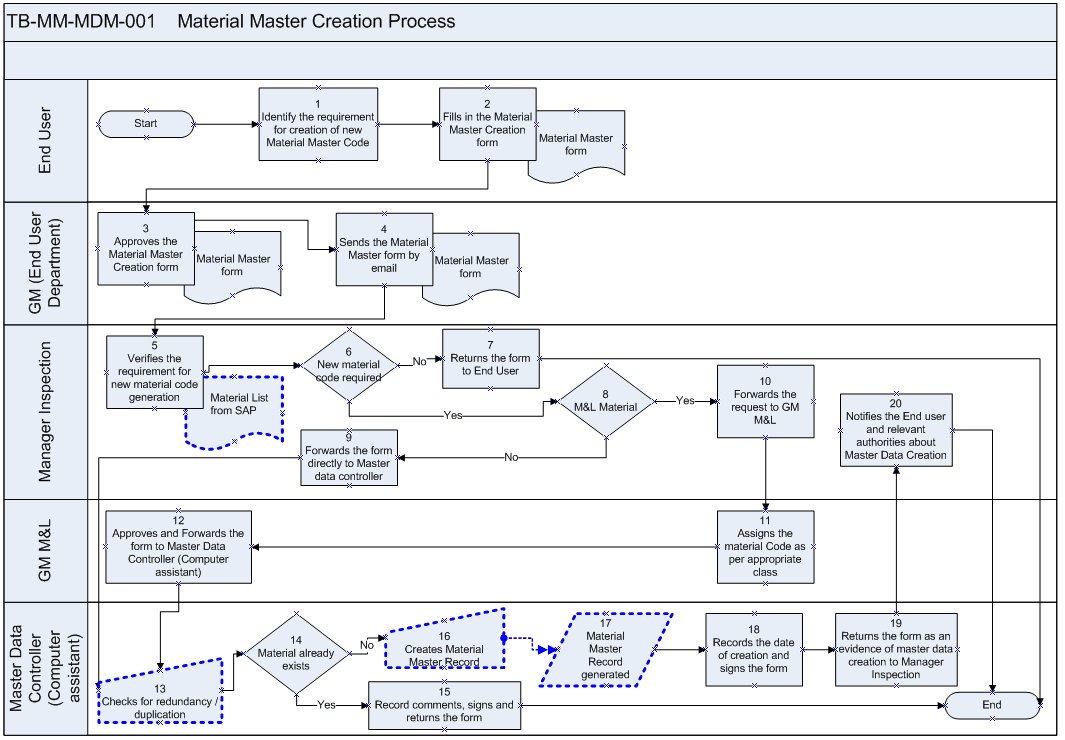
This flowchart illustrates the process for creating a new material master record in SAP, focusing on the flow of information and approvals between different departments. The process begins with a user identifying the need for a new material master and ends with the creation of the material master record in SAP and notification to relevant parties.
Process Steps explained further;
- End User (1, 2): The process starts with the End User department. It’s initiated when an end-user identifies the requirement for a new material master code (1). The End User then fills out the Material Master Creation Form (2).
- GM (End User Department) (3, 4): The completed form goes to the General Manager (GM) of the requesting department, who approves the Material Master Creation Form (3). The GM then sends the form to Manager Inspection by email (4).
- Manager Inspection (5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 20): The Manager Inspection verifies the requirement for the new material code generation using Material List from SAP (5). A decision point (6) checks if a new material code is actually required.
- No (6): If a new code isn’t needed, the form is returned to the End User (7).
- Yes (6): If a new code is required, another decision point (8) determines if it’s an M&L (Materials and Logistics) material.
- No (8): If not an M&L material, the form is forwarded directly to the Master Data Controller (Computer Assistant) (9).
- Yes (8): If it’s an M&L material, the request is forwarded to the GM M&L (10).
- Finally, the Manager Inspection notifies the End User and relevant authorities about Master Data Creation (20)
- GM M&L (10, 11, 12): If it’s an M&L material, the GM M&L receives the request (10), assigns the material code as per the appropriate class (11), and then approves and forwards the form to the Master Data Controller (Computer Assistant) (12).
- Master Data Controller (Computer Assistant) (13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19): The Master Data Controller checks for redundancy/duplication of the new materiel (13). A decision point (14) checks if the material already exists.
- Yes (14): If the material already exists, the Master Data Controller records comments, signs, and returns the form (15).
- No (14): If the material doesn’t exist, the Materiel Master Record is created in SAP (16), resulting in the Material Master Record being generated (17).
The Master Data Controller records the date of creation and signs the form (18). Finally, the form is returned as evidence of master data creation to the Manager Inspection (19).
Departments/Roles considered in Flowchart for Material Master Creation:
The flowchart is organized into swimlanes, each representing a specific department or role involved in the process:
- End User: Initiates the process by identifying the need for a new material master.
- GM (End User Department): Approves the material master creation form.
- Manager Inspection: Verifies the requirement for a new material code.
- GM M&L (Materials and Logistics): Assigns the material code if the material falls under M&L’s domain.
- Master Data Controller (Computer assistant): Responsible for checking redundancy, creating the material master record in SAP, and updating the form.
Related SAP Transactions/Functionality for Material Master Creation:
- Material Master Maintenance: MM01 (Create), MM02 (Change), MM03 (Display). The specific transactions used will depend on the fields being maintained.
- SAP Reporting: Used by Manager Inspection to verify material existence and prevent duplication (Material List from SAP).
Related Configuration/Settings for Material Master Creation in SAP:
- Material Type Configuration: Defines the characteristics and views for different material types (e.g., raw materials, finished goods).
- Number Range Configuration: Determines the number range used for assigning material numbers (internal or external).
- Field Selection Configuration: Controls which fields are required, optional, or hidden during material master creation.