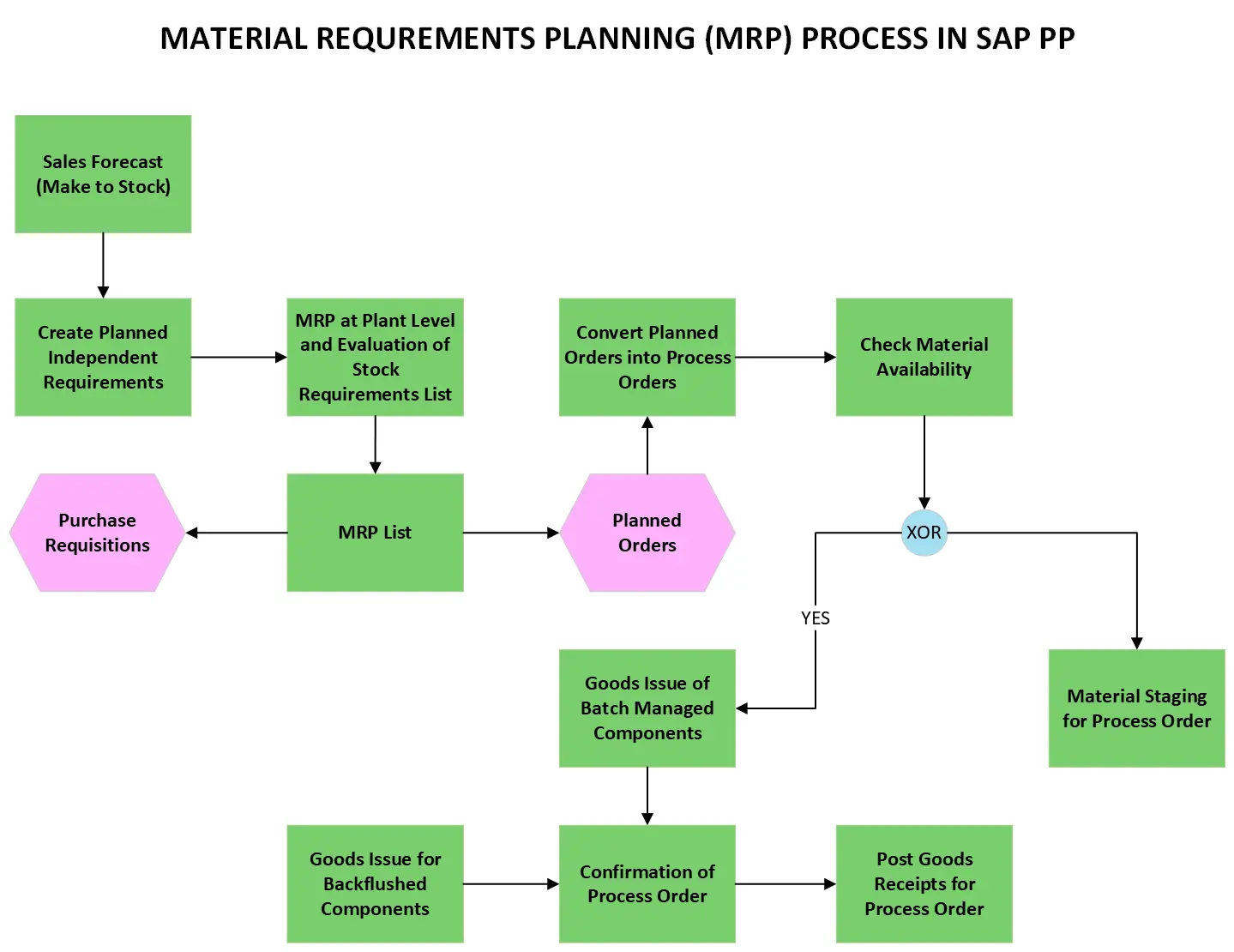
This flowchart shows Material Requirements Planning (MRP) process in SAP PP. It outlines the steps involved in ensuring you have the materials needed to produce finished goods, at the right time and quantity. Here’s a breakdown of the MRP process in SAP PP based on the flowchart:
- Sales Forecast (Make to Stock): The process begins with a sales forecast, which predicts future customer demand for finished goods. This is only applicable in a make-to-stock environment, where finished goods are produced based on anticipated demand.
- Create Independent Requirements: Based on the sales forecast (or other planning methods like production orders), planned independent requirements are created for the finished goods in the Production Planning (PP) module.
- Planned Independent Requirements List: The planned independent requirements list is created. This list includes the planned production quantities and dates for the finished goods.
- MRP at Plant Level and Evaluation of Stock Requirements: The system then runs MRP at the plant level. MRP considers various factors like the Bill of Materials (BOM), inventory levels, lead times, and planned independent requirements to determine the dependent requirements for all the materials required to produce the finished goods.
- MRP List: The MRP List is created after MRP is run at the plant level. This list includes the dependent requirements for all the materials needed to produce the finished goods. It specifies the required materials, quantities, and scheduled dates.
- Check Material Availability: The system checks the availability of materials in stock against the MRP list.
- Purchase Requisitions or Planned Orders: Depending on the availability of materials, the system creates either:
- Purchase requisitions for materials that need to be procured externally.
- Planned orders for materials that can be produced in-house.
- Convert Planned Orders into Process Orders: Planned orders for internally produced materials are then converted into production orders which can be scheduled on the shop floor.
- Goods Issue for Batch Managed Components: If the materials are batch-managed, a goods issue is made for the components required to produce the planned or production orders.
- Goods Issue for Backflushed Components: For backflushed components (components automatically consumed during production based on BOM quantities), a goods issue is made based on the confirmation of the process order.
- Post Goods Receipts for Process Order: Finally, the receipt of the finished goods produced is recorded in the system.