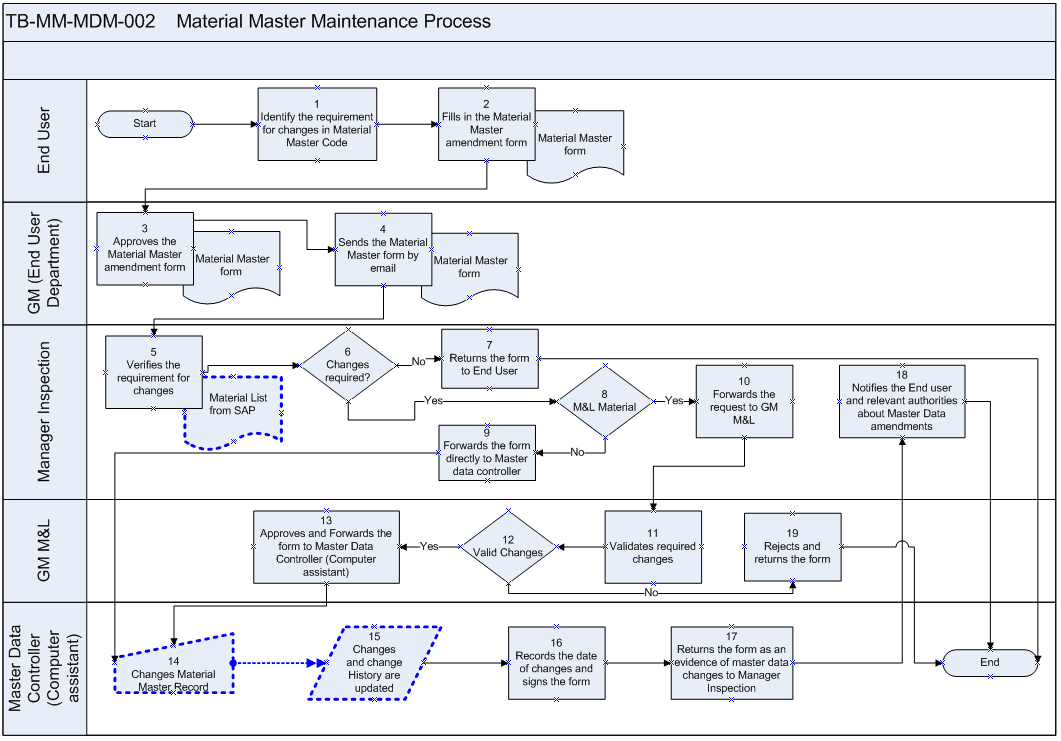
This flowchart outlines the process for requesting and implementing changes to Material Master data within the SAP system. It covers the steps involved from initial requirement identification by the end user to the final update of the Material Master record and notification of relevant parties.
In SAP ERP, the Material Master is a central repository of information for all materials used by a company. It contains descriptive data (e.g., material number, description, unit of measure), purchasing data, accounting data, and other relevant details. It’s essential for various business processes, including procurement, inventory management, and production planning.
Process Flow Descriptions:
- End User (Steps 1, 2):
- Identify Requirement (1): The process starts with the End User identifying the requirement for changes to a Material Master Code.
- Fills in Material Master Amendment Form (2): The End User then fills out the Material Master amendment form, detailing the required changes. This form can be used for creation, extension, or change requests (reference appendix MDM01).
- GM (End User Department) (Steps 3, 4):
- Approves the Material Master Amendment Form (3): The completed form goes to the General Manager (GM) of the requesting department, who approves the Material Master amendment form.
- Sends the Material Master form by email (4): The GM then sends the form to Manager Inspection by email.
- Manager Inspection (Steps 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 18):
- Verifies the requirement for changes (5): The Manager Inspection verifies the requirement for the changes using the Material List from SAP.
- Changes Required? (6): A decision point checks if the changes are actually required.
- If No: The form is returned to the End User (Step 7), ending the process.
- If Yes: Continues to the next decision point.
- M&L Material? (8): Another decision point determines if it’s an M&L (Materials and Logistics) material.
- If No: The form is forwarded directly to the Master Data Controller (Computer Assistant) (Step 9).
- If Yes: The request is forwarded to the GM M&L (Step 10).
- Step 18: Notifies the End User: Manager Inspection notifies the End User and relevant authorities about the Material Master amendments.
- GM M&L (Steps 10, 11, 12):
- Forwards the request to GM M&L (10): If it’s an M&L material, the GM M&L receives the request.
- Validates required changes (11): GM M&L validates the required changes.
- Valid Changes? (12): If GM M&L is not satisfied with the changes, the request is rejected, and the form is returned (Step 19).
- Approves and Forwards the form to Master Data Controller (13): After validating that the changes are valid and not duplicated, the GM M&L approves the form. It is then forwarded to the Master Data Controller (Computer Assistant).
- Master Data Controller (Computer Assistant) (Steps 14, 15, 16, 17):
- Changes Material Master Record (14): The Master Data Controller changes the Material Master record in SAP.
- Changes and change History are updated (15): The changes and change history are updated in the system.
- Records the date of changes and signs the form (16): The Master Data Controller records the date of creation and signs the form.
- Returns the form as an evidence of master data changes to Manager Inspection (17): Finally, the form is returned as evidence of master data changes to the Manager Inspection.