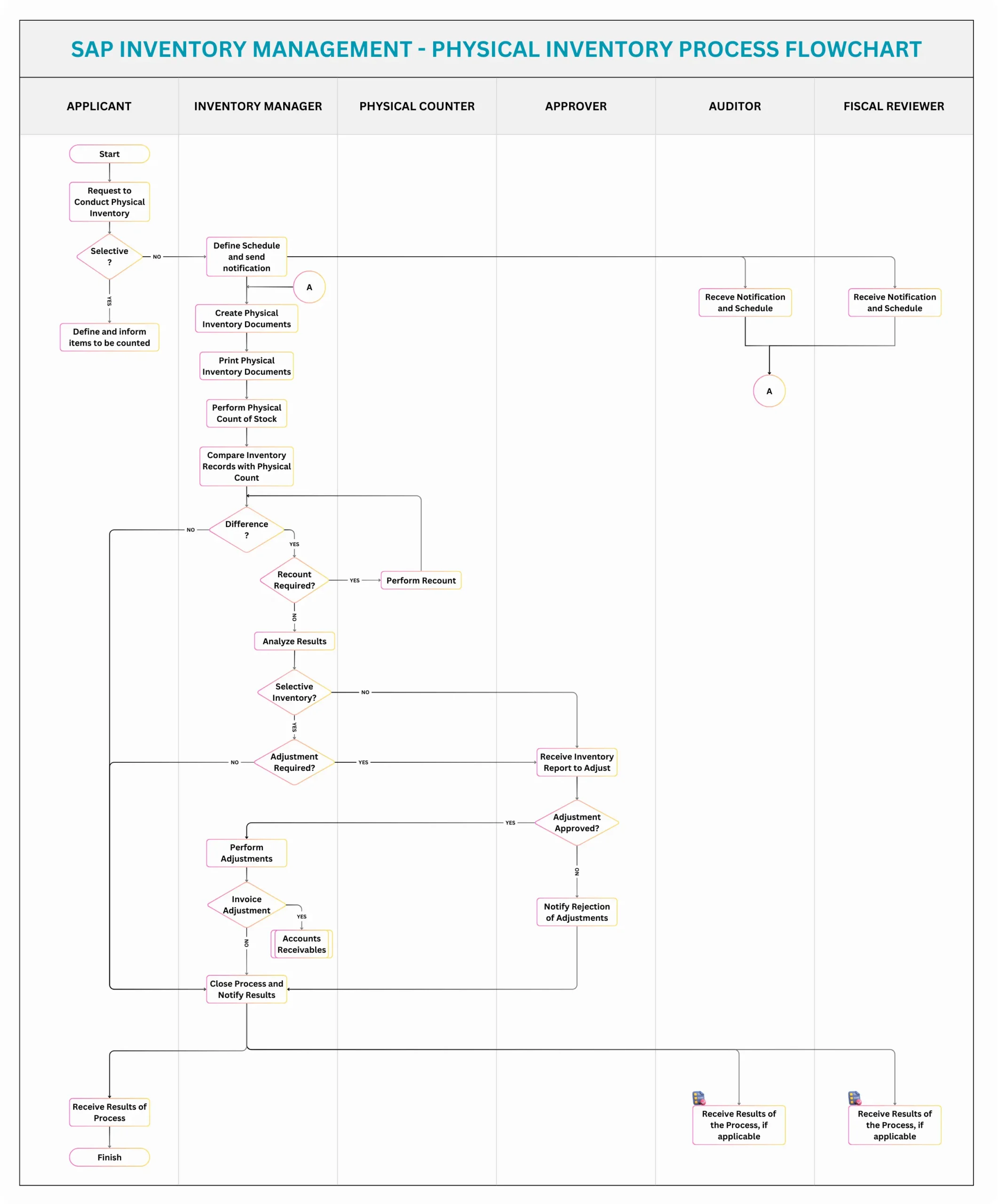
The core purpose of this SAP Physical Inventory process, as illustrated in the flowchart image, is to ensure the accurate recording of stock on hand by comparing system records with a physical count. The process encompasses several key stages, starting with the initiation and ending with the reconciliation and financial posting of any discrepancies. This process is primarily located within the MM (Materials Management) module, and it uses specific SAP transactions for efficient execution. The process aims to create reliable inventory reports that highlight and value discrepancies, as well as maintain a statistical record of the differences for proper accounting.
Key Stages of the Process:
- Initiation and Planning:
- The process begins with a request by an Applicant to conduct a physical inventory, which can be either “Selective“, focused on a subset of materials or stock, or a broader scope.
- The Inventory Administrator is responsible for planning when the inventory is to be carried out and sends a notification to the rest of participants.
- This planning phase involves defining a schedule, the scope of materials and/or stocks to be counted and if blocking of stock movements are necessary.
- Document Creation:
- The process involves the creation of an Inventory Document using the MI01 transaction. This document is central to the process as it specifies what’s being counted, when, and where.
- During the document creation, the administrator configures inventory settings and parameters like blocking of postings for stock movements during count, snapshotting the book stock (theoretical stock) and more.
- It is also possible to filter materials or groups directly from the SAP interface and include previously inventoried materials and/or material lots.
- The printing of Physical Inventory Documents is done usually via MI21 for paper based recording methods.
- Physical Counting:
- The Physical Counter is tasked with physically counting the designated materials at the specified storage locations, after being notified and scheduled with the documents to count.
- This involves comparing with printed lists and physically recording the actual count as per requirements.
- Data Entry and Comparison:
- The physical counts recorded are then entered into SAP using the MI04 transaction.
- SAP then compares these physical counts with the current book stock (system inventory), which were snapshotted or recorded previously and highlights any differences.
- Variance Analysis and Adjustments:
- The system lists and displays differences using transaction code MI20. With this, it’s possible to modify a count that’s wrong, or proceed with booking the variances.
- If significant discrepancies are found or require corrections, it is possible to go back and Perform Recount activities and re-enter counts.
- These discrepancies require review using MI03 or similar transactions, to ensure correct status and material data is used.
- Depending of the results of this analysis, Inventory Adjustments may be required. In this case, the process requires a formal approval.
- Financial and Inventory Posting:
- Once adjustments are approved: the inventory adjustments are posted on SAP, which updates system records using MI07 transaction and generates accounting documents with reference to inventory differences identified.
- This reconciliation requires financial posting using movement reasons (701 for gain and 702 for losses), allowing the system to properly update the financials.
- After posting, a Material Document is also generated that can be reviewed usually through MIGO transaction. The material document shows a trace of the material stock adjustments made due to identified discrepancies in a physical inventory
- Process Closure and Reporting:
- Finally, the system and manual processes conclude with proper reporting, which is distributed with approvals needed to Auditors and Fiscal Reviewers.
- This ensures a documented record of all inventory activities, supporting both operational and audit requirements.
- The process concludes by Closing the process, a step that also ensures accurate results for finance.
Key SAP Transactions Involved:
This process has several key SAP transactions which include but aren’t limited to:
- MI01: Create inventory document
- MI02: Change inventory document
- MI04: Enter inventory count
- MI07: Post inventory differences
- MI20: List of inventory differences
- MI21: Print inventory document
Roles and Responsibilities:
The process also incorporates a number of roles: an Applicant who initiates the process, an Administrator who plans and controls process steps, a Physical Counter who conducts the physical count, an Approver who verifies, an Auditor, and an External Fiscal Reviewer, who oversees the proper documentation of assets.
In Summary:
This process overview details the procedural steps to ensure a smooth and compliant physical inventory. It emphasizes the efficient management of discrepancies between the system inventory records and physical counts, using a combination of system actions and manual intervention. By using the listed SAP transactions, this process supports companies in maintaining inventory accuracy and compliance.
📚 Further Related SAP Documentation: