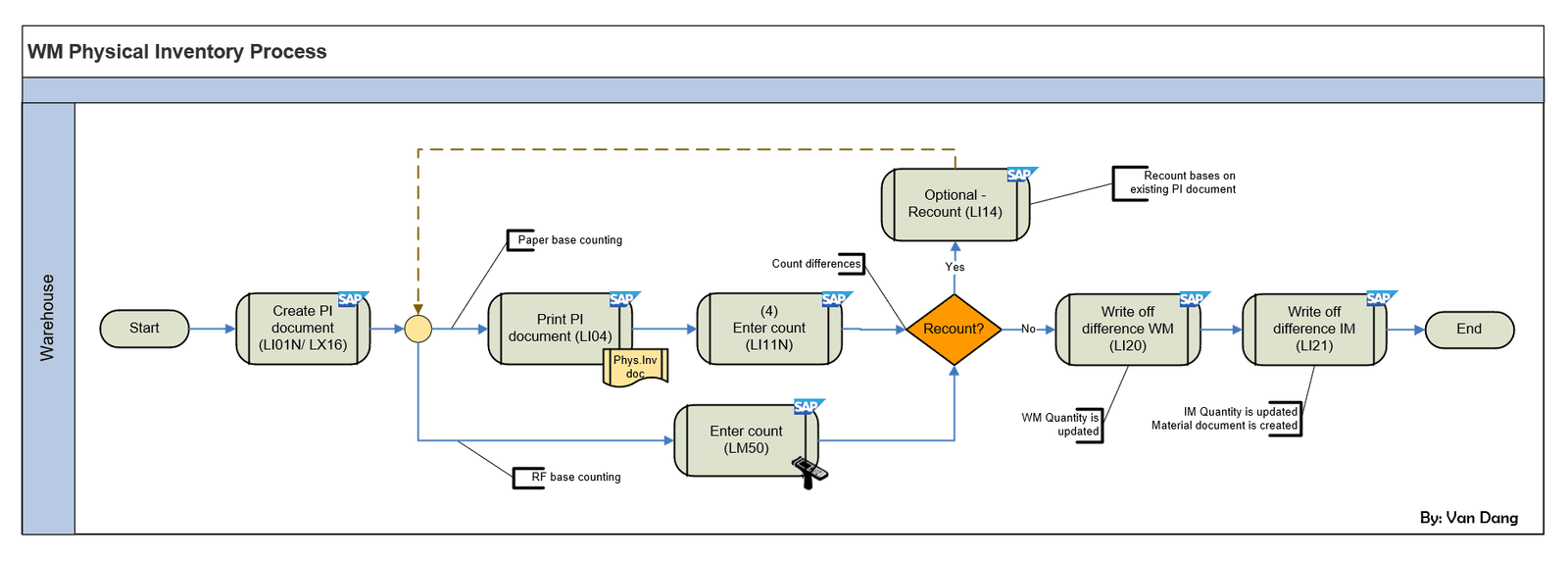
The SAP Warehouse Management (WM) Physical Inventory Process is a crucial procedure for maintaining accurate inventory records within a warehouse environment. This process ensures that the physical stock matches the system records, which is essential for effective inventory control and operational decision-making. The flowchart, created by Dang_Bao_Van, provides a visual representation of the various steps, transaction codes, and decision points involved. Below is a detailed breakdown of the flowchart.
1. General Overview
The flowchart outlines the steps required to conduct a physical inventory count using SAP WM. It includes creating Physical Inventory (PI) documents, entering count results manually or via RF devices, handling discrepancies at both WM and IM levels, and utilizing various SAP transaction codes to manage these activities. The primary SAP transactions involved include:
- LI01N/LX16: Creation of PI documents.
- LI04: Printing PI documents.
- LI11N: Entering count results manually.
- LM50: Entering count results using RF devices.
- LI14: Recounting if necessary.
- LI20: Writing off differences at the WM level.
- LI21: Writing off differences at the IM level.
- LX25: Inventory status overview at the bin level.
- LX22: Physical inventory lists and status.
2. Detailed Flow Diagram Breakdown
Step 1: Create PI Document (LI01N/LX16)
- LI01N (Create PI Document): This transaction code is used to manually create a PI document for specific storage bins. Users enter bin numbers individually, which is beneficial when checking specific storage bins are needed.
- LX16 (Create PI for Continuous Inventory): This method allows for the creation of multiple PI documents simultaneously by selecting bins based on a specific storage type. This streamlines the documentation phase, especially for warehouses with extensive inventories.
Regardless of the method chosen, the PI document is created and activated, serving as the official record for the physical inventory count. The storage bins are blocked to prevent any stock movement until inventory is complete.
Step 2: Print PI Document (LI04)
- LI04 (Print PI Document): This step is optional but recommended for maintaining a physical record or for verification purposes. Printing the PI document provides a tangible inventory list that can be used during the physical counting process.
Step 3: Enter Count (LI11N/LM50)
- LI11N (Enter Count Manually): After conducting the physical count, the results are manually entered into the system using this transaction code. Each line item within the PI document is updated with the corresponding counted quantity. Lines with zero counts are marked accordingly.
- LM50 (Enter Count with RF Devices): This transaction uses RF gun for the counting, which first requires the assignment of the UserID to the PI Document. Using RF device can streamline the input process, especially in larger warehouses.
- Process with RF devices:
- Scan the Bin to start the count
- Scan HU one time to register it’s in the scanned bin
- Scan HU second time will trigger screen to enter quantity, and option to mark as zero if not applicable, press F9 when you finish the count.
- Process with RF devices:
Step 4: Decision Point – Recount?
At this juncture, a decision is made based on the accuracy of the entered count:
- Yes: If significant discrepancies are detected, a recount is initiated using LI14. This step involves re-evaluating the physical stock to ensure accuracy.
- No: If the count is deemed accurate or discrepancies are within acceptable limits, the process proceeds to write off any differences.
Step 5: Write Off Difference WM (LI20)
- LI20 (Clear off at WM level): This transaction is used to post any differences between the counted quantities and the system quantities at the WM level.
- Key Actions: This step updates the WM quantities, and unblocking the storage bin. It is important to note that a material document is not created in this phase.
Step 6: Write Off Difference IM (LI21)
- LI21 (Clear off at IM level): This transaction is used to post any differences between the counted quantities and the system quantities at the IM level.
- Key Actions: This step updates the quantities at the Inventory Management level and creates a material document to record the stock adjustments.
Step 7: Informative Reporting
To monitor and analyze inventory discrepancies, SAP provides reporting tools:
- LX25 (Inventory Status at Bin level): This report provides an overview of the inventory status at the bin level.
- LX22 (Physical Inventory List and status): This report generates a comprehensive list of all physical inventory documents, displaying their statuses.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively manage their physical inventory process within SAP WM, ensuring accurate stock records and operational efficiency.