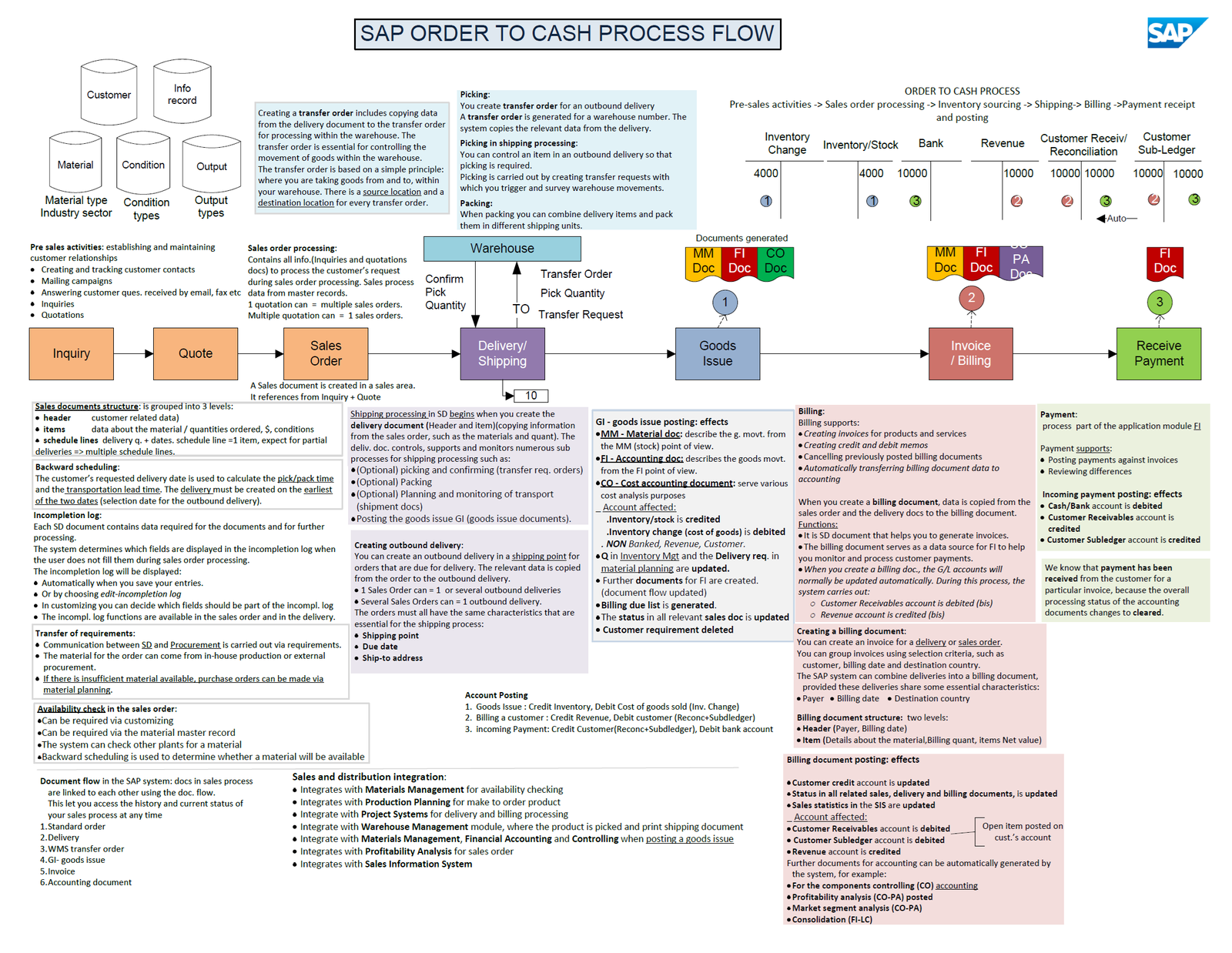
The SAP Order-to-Cash process is a critical component of any organization’s operations. It encompasses all the steps involved in converting sales orders into cash receipts. Key stages of the SAP Order-to-Cash process flow are explained in detail, as depicted in the image;
Key Stages of the SAP Order-to-Cash Process
- Presales Activities: This stage involves building and maintaining customer relationships. It includes activities like creating and tracking customer contacts, answering customer inquiries, and conducting mailing campaigns.
- Sales Order Processing: In this stage, sales orders are created and processed. The system checks product availability, creates delivery dates, and generates picking and shipping documents.
- Inventory Sourcing and Fulfillment: This stage involves sourcing the necessary inventory to fulfill the order. It includes activities like creating transfer orders, picking, packing, and shipping the goods.
- Billing and Payment Receipt: This stage involves creating and sending invoices to customers and receiving payment. It includes activities like generating billing documents, posting goods issues, and reconciling payments.
Key Notes of the SAP Order-to-Cash Process
📄 Sales Document Structure: Sales documents in SAP are structured into three levels:
- Header: Contains customer-related data
- Items: Includes data about the material, quantities ordered, prices, and conditions
- Schedule lines: Details delivery quantities and dates. Each item typically has one schedule line, except for partial deliveries which may have multiple schedule lines.
🚚 Shipping and Delivery: Shipping processing is a critical phase that begins with creating the outbound delivery document. This document controls various sub-processes:
- Optional picking and confirming (transfer request orders)
- Optional packing
- Optional planning and monitoring of transport (shipment documents)
- Posting the goods issue (GI)
The creation of a transfer order is essential for controlling the movement of goods within the warehouse, specifying source and destination locations for every transfer.
💼 Billing: Billing is a crucial step that bridges sales and financial processes. Key functions include:
- Creating invoices for products and services
- Generating credit and debit memos
- Cancelling previously posted billing documents
- Automatically transferring billing document data to accounting
When a billing document is created, the system updates several accounts:
- Customer Receivables account is debited
- Revenue account is credited
- Customer Subledger account is updated
💰 Payment Processing: Payment processing, handled in the FI module, involves:
- Posting payments against invoices
- Reviewing differences
- Updating relevant accounts (Cash/Bank account debited, Customer Receivables and Subledger accounts credited)
O2C Integration with Other SAP Modules: The O2C process demonstrates SAP’s integrated approach, connecting with various modules:
- Materials Management (MM): For availability checking and inventory management
- Production Planning (PP): For make-to-order products
- Financial Accounting (FI): For invoice and payment processing
- Controlling (CO): For cost analysis and profitability
- Warehouse Management (WM): For picking and shipping operations
- Profitability Analysis (CO-PA): For sales order analysis
This integration ensures seamless data flow and process consistency across the organization.
Order to Cash Document Flow in SAP
SAP maintains a clear document trail throughout the O2C process, linking:
- Standard order
- Delivery
- WMS transfer order
- Goods issue
- Invoice
- Accounting document