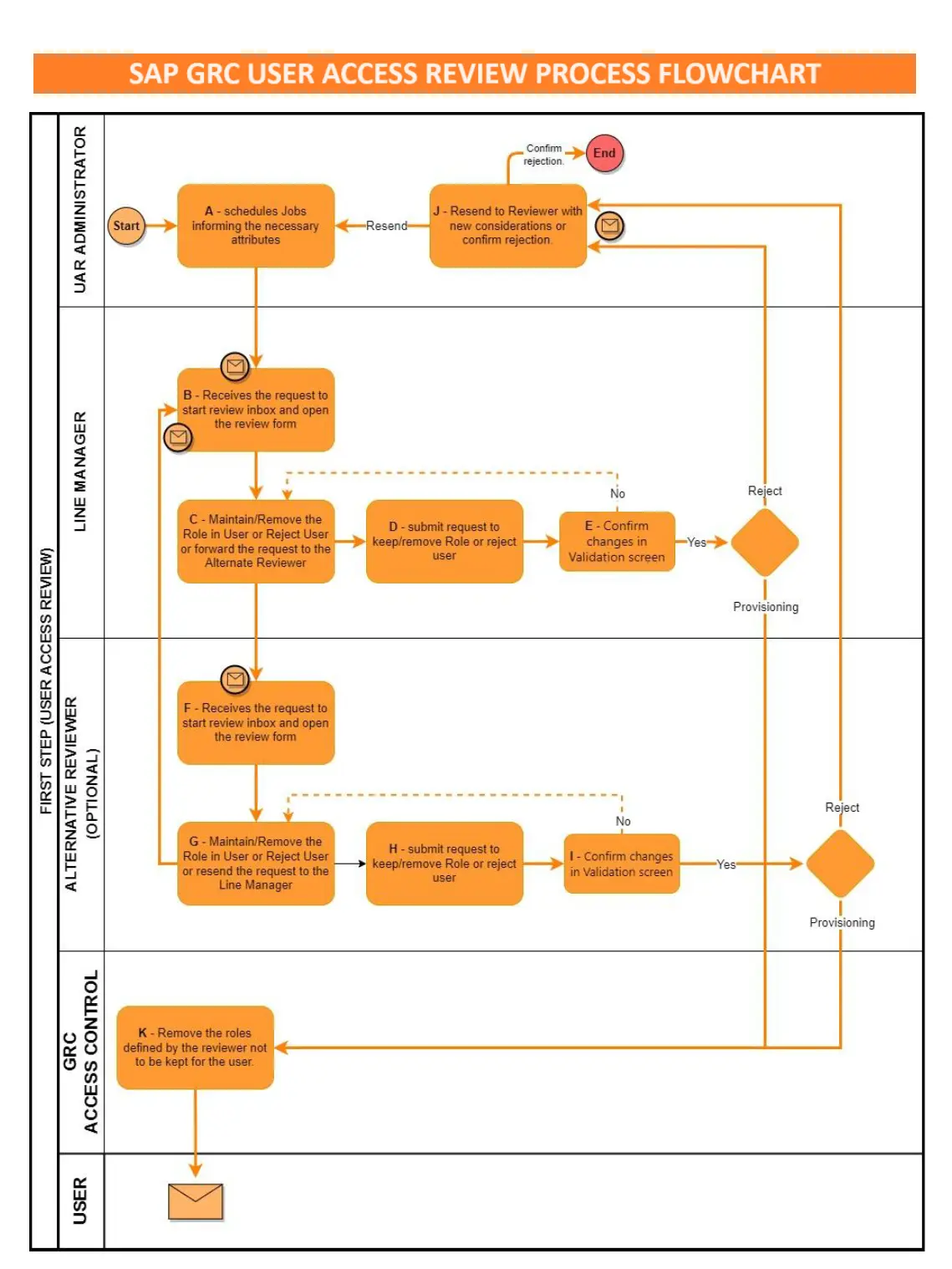
This flowchart represents an SAP User Access Review (UAR) process, which is a review cycle usually undertaken to ensure that SAP system users have the appropriate access rights. It is particularly relevant for compliance and governance within an organization. The steps are segregated across three different roles: UAR Administrator, Line Manager/Alternate Reviewer, and GRC Access Control.
Flowchart Process Description:
- Start (Administrator) 🔄: The process begins with the Administrator programming the job for creating the revision request.
- Receive Request (Line Manager) 📬: Upon creation, the Line Manager receives the request to begin the review by opening the review form.
- Set Access (Line Manager) 🔧: The Line Manager then determines whether to maintain or remove the user’s role or to reject the user outright. The request can also be forwarded to an Alternate Reviewer if needed.
- Submit Request (Line Manager) 📤: After reviewing, the Line Manager submits the request to either keep/remove the Role or to reject the user.
- Confirm Changes (Line Manager) ✅: The Line Manager must confirm the changes in the Validation screen, ensuring all actions from the previous session are correct.
- Receive Request (Alternate Reviewer) 📬: If the request is forwarded, the Alternate Reviewer receives it and opens the review form.
- Set Access (Alternate Reviewer) 🔧: Similarly, the Alternate Reviewer can maintain/remove the role in the User or reject the User, and can save and resend to the original Reviewer.
- Submit Request (Alternate Reviewer) 📤: The Alternate Reviewer submits the request to keep/remove the Role or reject the user after their review.
- Confirm Changes (Alternate Reviewer) ✅: The Alternate Reviewer confirms the changes in the Validation screen, checking that all actions are in order.
- Review Rejections (Administrator) 🔍: If there are any rejections, the Administrator reviews them and decides whether to resend to the reviewer or to confirm and explain the reason for rejection.
- Provisioning (GRC Access Control) 🛠️: Finally, the GRC Access Control removes the roles defined by the reviewer that are not to be kept for the user, concluding the process.
Throughout the flow, there are decision points where the request can be rejected, which leads to a validation of the rejection and potential resending for reconsideration. The process is cyclic, meaning that the steps can be revisited based on decisions made at various stages. The ultimate goal of this flow is to ensure that the user’s access rights in the SAP system are current, necessary, and compliant with organizational standards.