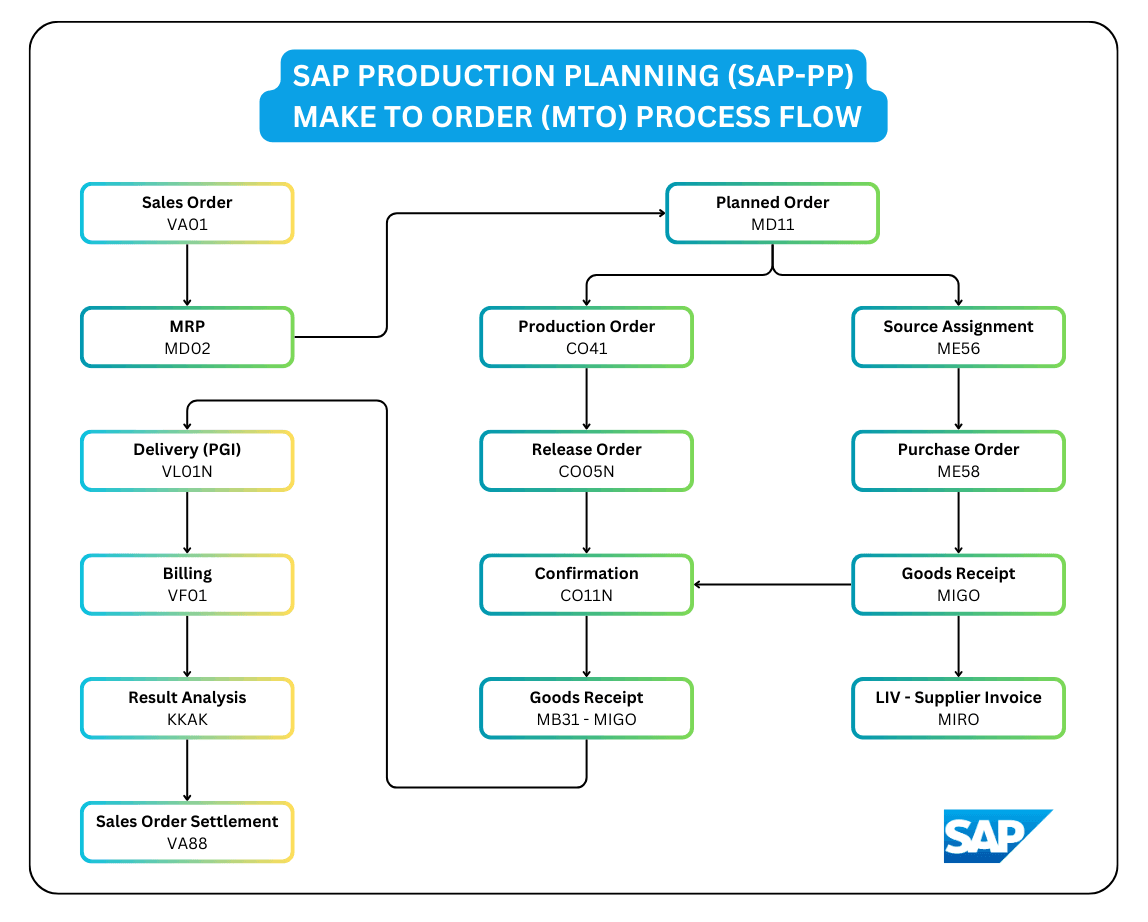
This flowchart depicts the Make to Order (MTO) process in SAP, showing the flow of activities and data across different modules, specifically SD (Sales and Distribution), MM (Materials Management), PP (Production Planning), and CO (Controlling). It uses a top-down approach, starting with a sales order and branching out to production and procurement activities. The flowchart also includes costing and settlement. A detailed breakdown of each component of the flowchart is provided below with related transaction codes (tcodes):
- Sales Order (VA01):
- The process begins with the creation of a sales order using transaction VA01.
- This sales order uses document type ‘OR’, requiring a distribution channel and division. It also involves determining shipping points based on loading group and shipping conditions. Requirement type ‘KEV’ is triggered, and the account assignment category is ‘M’.
- Availability check and scheduling are performed.
- Costing is initiated, using a valuation class that determines costing accounts. Costing is marked to be used in result analysis.
- MRP (MD02):
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is run using transaction MD02, generating planned orders based on sales order demand.
- The process can be run for either a project or plant level and produces both ‘in-house’ or ‘external’ planned orders based on the material’s procurement type.
- Strategy group 50, requirement class, and special stock settings are configured. The production version is a mandatory setup.
- Planned Order (MD11): The MRP run creates Planned Orders using transaction code MD11.
- Production Order (CO41):
- The planned order is converted into a production order using transaction CO41.
- This can be done individually or as a collective process.
- Production version assignment is required during this process.
- Release Order (CO05N): Production order is released using transaction CO05N, usually through mass processing.
- Confirmation (CO11N):
- Production activities are confirmed using transaction CO11N, involving component issues.
- Goods movement from special stock happens with the relevant movement type.
- Goods Receipt (MB31 – MIGO): After production, a goods receipt is posted using transaction MB31 or MIGO, the goods receipt is posted to customer stock and an accounting document is created.
- Source Assignment (ME56): Planned orders are converted to purchase requisitions. Sources are assigned using transaction ME56, utilizing source lists and info records.
- Purchase Order (ME58): The purchase requisition is converted into a purchase order using transaction ME58.
- Goods Receipt (MIGO): A goods receipt is posted using MIGO upon delivery by the supplier.
- LIV – Supplier Invoice (MIRO): Supplier invoice verification is done using transaction MIRO.
- Goods Receipt (MB31 – MIGO): The in-house produced goods receipt from step 7 converges with the external procurement, which is ready with goods after step 10. This second goods receipt is for the finished good.
- Delivery (PGI – VL01N): Finished goods are delivered using transaction VL01N, creating a delivery document and includes a Post Goods Issue (PGI). Shipping point, storage location, and loading groups are required.
- Billing (VF01): The delivery document is used for billing via transaction VF01. The billing process uses condition type PR00 (or similar), and an accounting document is created.
- Result Analysis (KKAK): Result analysis is carried out using transaction KKAK to determine WIP and other values.
- Sales Order Settlement (VA88): Sales order settlement is done via transaction VA88, settling costs and revenue. Direct costs can also be assigned to the sales order. This process transfers cost and revenue to CO-PA.
The flowchart illustrates the steps in a Make-to-Order process within SAP. The process covers both in-house and external procurement, converging at goods receipt before proceeding to delivery, billing, and final settlement.
It’s very useful process flow.