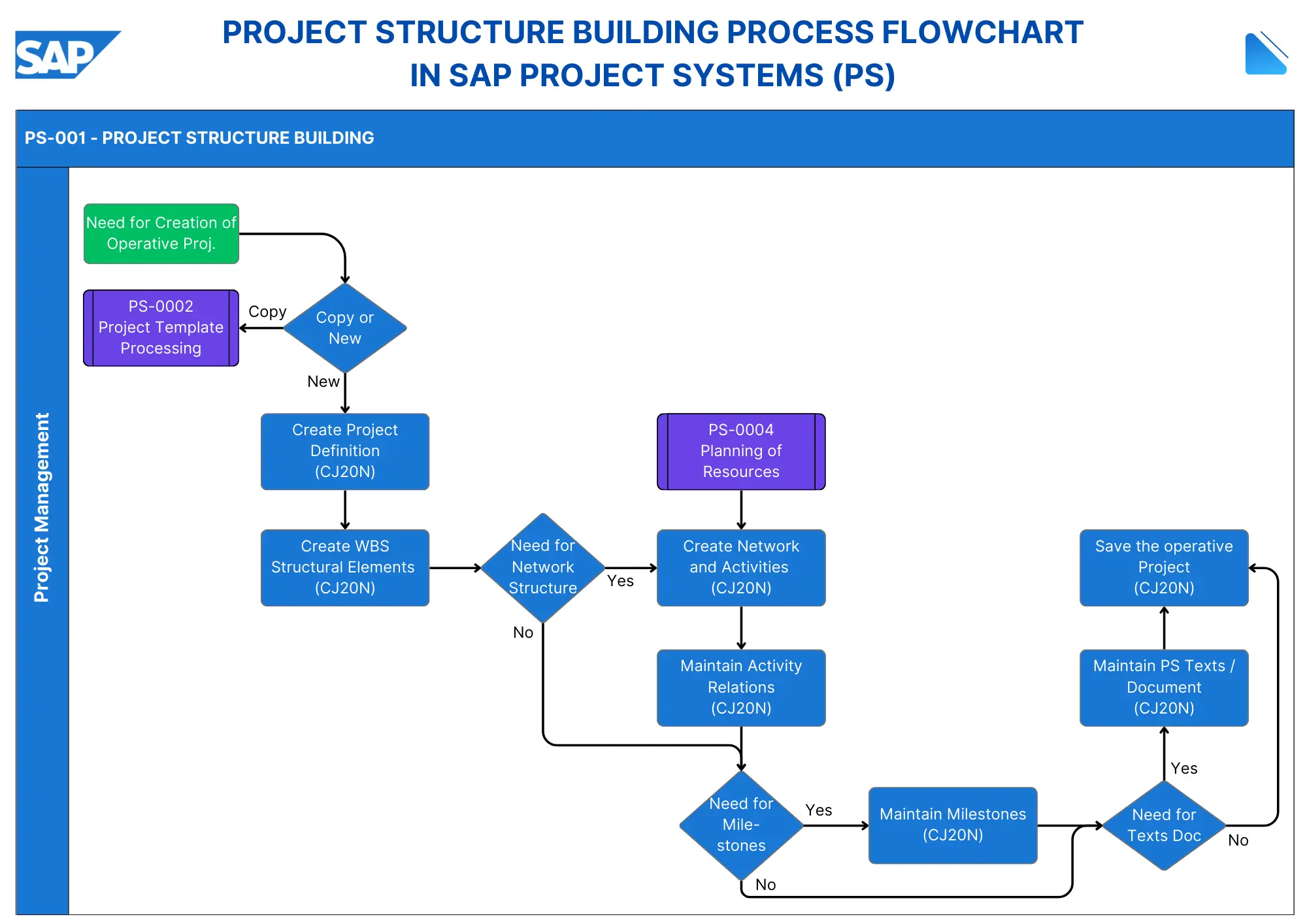
The SAP Project Structure Building Process within the Project Systems (PS) module is a systematic approach to creating and managing project structures. This process involves several key steps, each contributing to the overall project management lifecycle.
Below is a detailed description of the sequential steps involved in the attached flowchart image, including decision points that ensure project requirements are adequately assessed.
SAP Project Structure Building Process Steps:
- Need for Creation of Operative Project: The process begins with a requirement to create an operative project, initiating project setup in SAP.
- Project Template Processing: Optionally, a project template can be processed to serve as a base for the new project. This template provides a predefined structure, reducing setup time.
- Copy or Create New Project: A decision is made to either copy an existing project template or start a new project from scratch.
- Create Project Definition (CJ20N) 📘:The process begins with establishing a Project Definition, which serves as the overarching framework for the project. This definition includes critical data such as start and end dates, organizational units (company code, profit center, etc.), and planning parameters that affect all subsequent project components. It acts as a control basis for overall project management, allowing default values to be passed on to Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) elements.
- Create WBS Structural Elements (CJ20N) 🔧: Following the project definition, WBS elements are created to represent the project’s activities in a hierarchical structure. Each WBS element can be detailed at various levels until the desired granularity is achieved. This hierarchical model facilitates effective planning of costs, revenues, scheduling, and budgeting. Additionally, WBS elements can be assigned specific organizational units such as profit centers and cost centers for reporting purposes.
- Need for Network Structure 🔄: A decision point determines whether the project requires a network structure. If network activities are needed, the process proceeds to the next step; otherwise, it skips to the milestone decision.
- Planning of Resources: Resource planning is conducted, setting the groundwork for creating network activities by identifying required resources.
- Create Network and Activities (CJ20N) 🛠️: Next, networks are established to represent individual project activities along with their temporal and logical relationships. Each network comprises activities that describe the specific tasks involved in the project. These activities are linked through relationships that define their sequence and dependencies, forming the operative basis for planning dates, costs, and resource allocation.
- Maintain Activity Relations (CJ20N) 🔗: This step involves establishing relationships between activities within the network. Various types of relationships can be defined, such as start-to-start or finish-to-start, which dictate how tasks are interdependent and their sequencing. Properly maintaining these relationships is crucial for accurate scheduling.
- Need for Milestones: A decision is made on whether the project requires milestones to track major achievements. If needed, milestone maintenance follows; if not, the process continues to document maintenance.
- Maintain Milestones (CJ20N) 📅: Milestones are then established to mark significant events or deadlines within the project timeline. Assigning milestones to activities allows for tracking crucial progress points and can facilitate milestone billing in financial processes. This step ensures that important achievements are documented and monitored throughout the project’s lifecycle.
- Need for Texts/Document: A final decision determines if any additional text or document maintenance is required. If yes, the process proceeds to the next step; if no, it goes directly to saving the project.
- Maintain PS Texts / Document (CJ20N) 📄: Essential documentation is maintained during this phase by assigning user-definable texts to WBS elements or activities. This documentation can include project structure texts managed in a catalog or external documents stored using the SAP Document Management System (DMS). Effective documentation aids in communication and provides context for project stakeholders.
- Save the Operative Project (CJ20N) 💾: The final step in this process is saving the operative project once all elements have been defined and established. This action finalizes the project setup in SAP PS, allowing for ongoing management and execution of tasks as planned.
This flowchart effectively represents the structured process in SAP Project Systems for building project components, emphasizing project setup, WBS creation, network activities, milestone management, and documentation. The steps, enhanced with decision points, ensure a tailored project structure based on specific requirements.