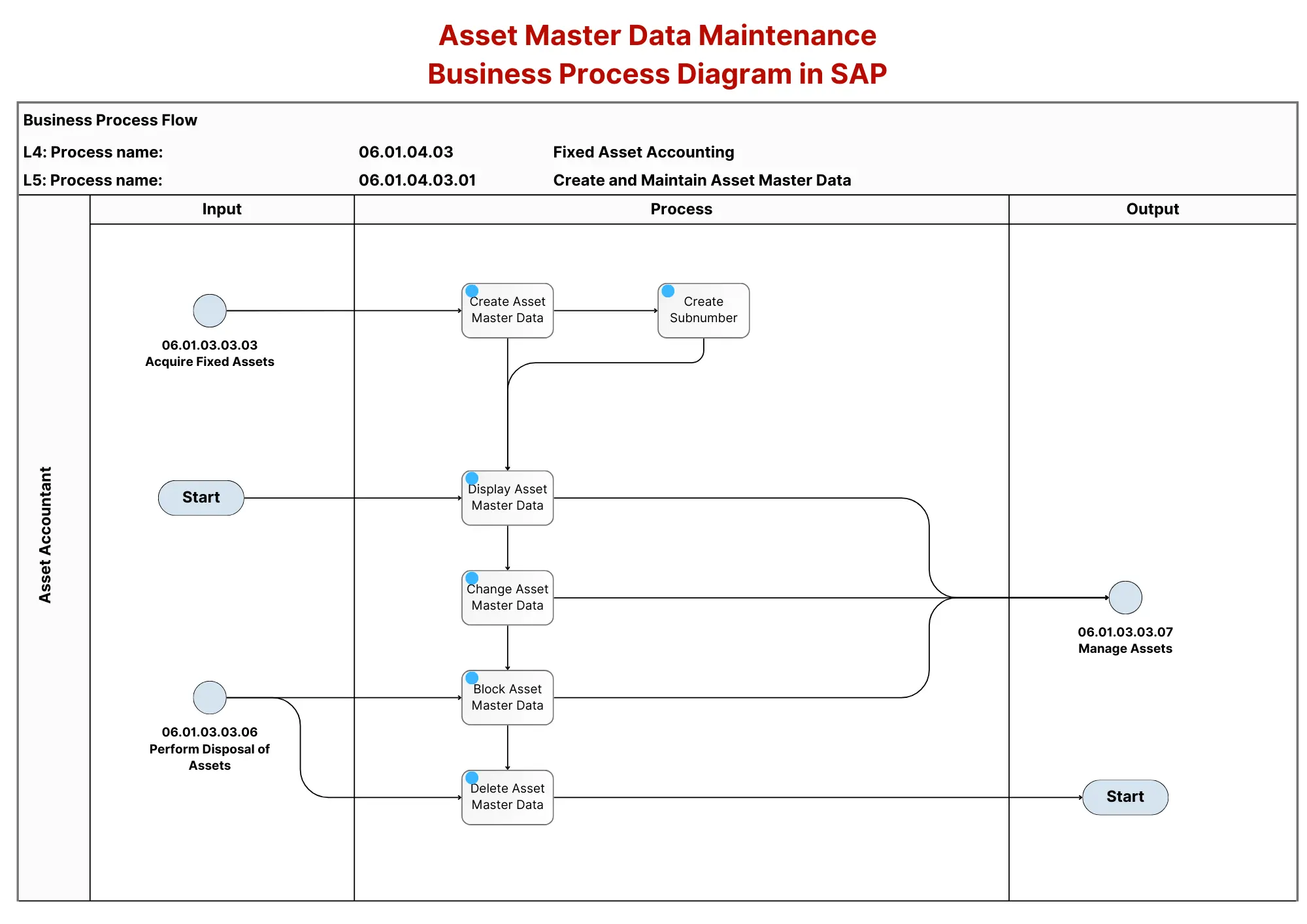
This process focuses on creating and managing Asset Master Data within SAP FI-AA, which refers to the detailed information an organization maintains about its fixed and intangible assets. The flowchart provided in the image outlines the steps performed primarily by the Asset Accountant to manage this data. Below is a breakdown based on the detailed process steps from the document:
- Create Asset Master Data 🛠️: The process begins with the creation of a new asset in SAP, either for a single asset or a group asset. This data is essential for tracking asset information throughout its lifecycle, including financial postings and depreciation.
- Create Subnumber for Asset 🔢:A subnumber is created to manage components of an asset separately. This is useful for tracking different asset components individually, for example, if they are assigned to different cost centers.
- Display Asset Master Data 📊: This step involves viewing existing asset master data without making any changes. It allows the Asset Accountant to access the current details of an asset as recorded in the system.
- Change Asset Master Data ✏️: Changes are made to the asset master data, such as updating the account assignment or modifying time-dependent information like cost centers or depreciation parameters.
- Block Asset Master Data 🚫:The asset master data is blocked to prevent it from being used in further transactions. This is typically done when the asset is no longer active but still needs to be retained in the system for historical purposes.
- Delete Asset Master Data 🗑️: This step removes asset master data from the SAP system, generally due to the asset being disposed of or made obsolete, ensuring it is no longer available for any transactions.
These steps form the core process for managing asset master data within SAP, from creation through to potential deletion, ensuring the proper handling of asset information throughout its lifecycle.