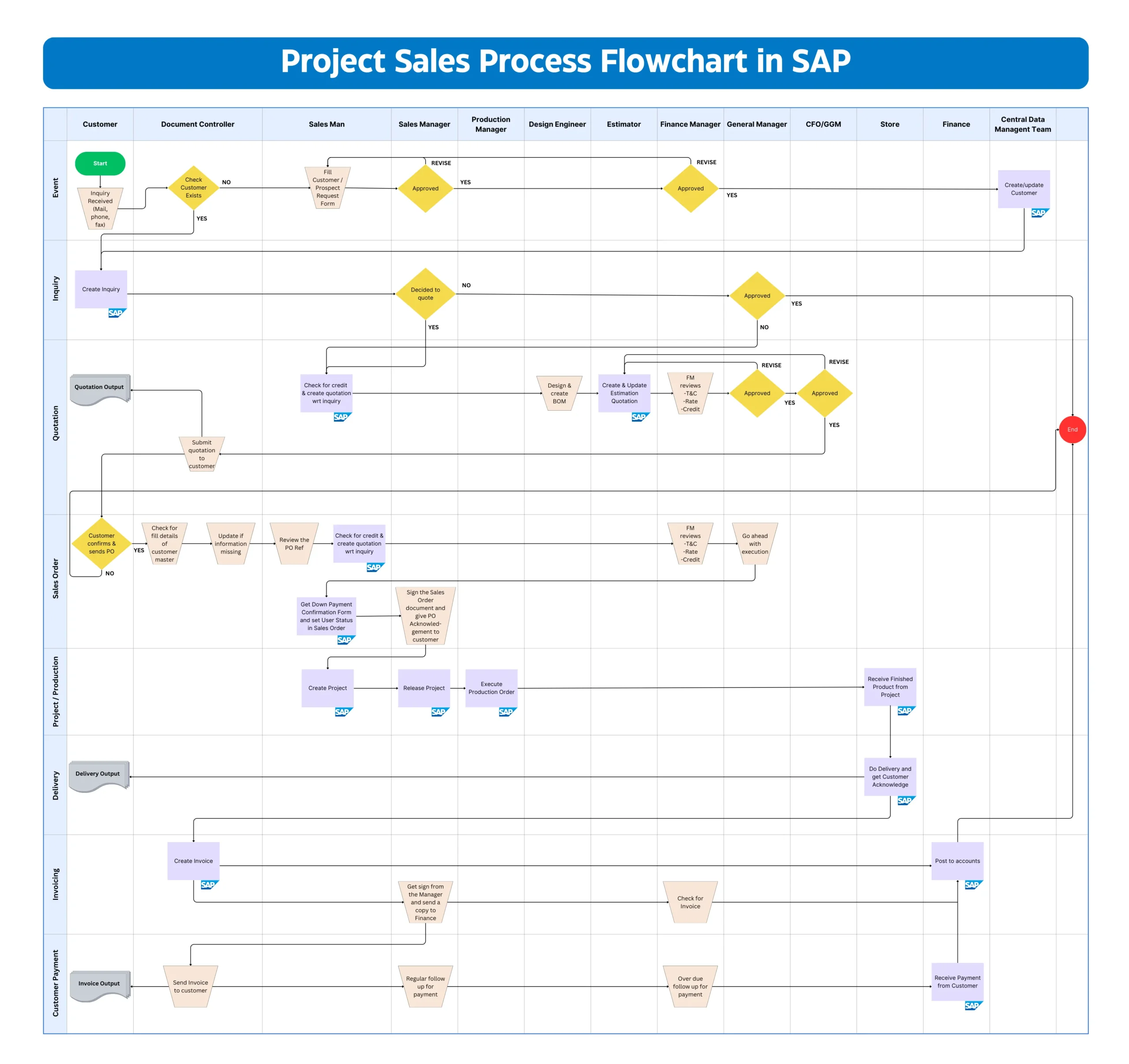
This flowchart illustrates the end-to-end (E2E) Project Sales process in SAP Order to Cash (O2C) Cycle, designed for a metal fabrication and manufacturing company specializing in custom-engineered products such as pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and structural steel components.
The flowchart is structured organizational roles wise, illustrating how responsibilities and tasks flow between different departments throughout the project lifecycle in SAP.
A detailed explanation of the process shown in the flowchart:
- 📞Customer Inquiry: The project sales cycle begins when a potential client submits an inquiry, often detailing complex technical specifications for custom-engineered products. This crucial first step is captured in the SAP system, recording:
- Customer or prospect identifier (new codes are created for first-time inquiries)
- Material specifications (using existing codes or creating placeholders for new designs)
- Requested quantities and units
- Client’s expected response timeline
This digital record initiates the internal workflow, alerting relevant departments like engineering and sales to begin preliminary assessments.
- 🛠️Material Set up and Costing: Upon receiving the inquiry, a multi-faceted process begins to translate the client’s requirements into actionable production data:
- Creating or updating material master records for the finished product
- Developing a comprehensive Bill of Materials (BOM), detailing all components
- Establishing the production routing, defining each step in the manufacturing process
- Conducting detailed product costing, factoring in materials, labor, and overhead
This stage is critical for accurate quoting and forms the foundation for potential project execution.
- 💼Quotations: Once the final cost is determined, a quotation is generated within the system. A quotation serves as a legally binding offer, outlining the terms for delivering a product or service within specific conditions and valid for a designated period. The system allows for the creation, viewing, and evaluation of quotations in a list format. You can utilize selection criteria to refine the list, enabling more focused display and processing. For analytical purposes, you can review all quotations processed within a given timeframe and examine those that were rejected, along with the corresponding reasons.
With costing complete, the sales team crafts a detailed quotation in SAP. This document serves as a formal offer, outlining:
- Specific sales area and organizational details
- Client information and validity period
- Detailed material descriptions and quantities
- Comprehensive pricing structure, including any special conditions
- Proposed payment and delivery terms
- Relevant stakeholders (e.g., ship-to, bill-to parties)
The quotation undergoes internal approvals based on value thresholds before being presented to the client.
- 📋Sales Order Creation: The sales order serves as a record of the customer’s order, capturing essential details. Purchase order (PO) information is recorded at the header level of the sales order. Prior to creating a sales order, a project must be established in the system, along with a milestone billing plan. The billing percentages associated with each milestone are defined within the project. A sales order can be created independently or based on a quotation. If the quotation was generated for a prospect, the prospect must be converted into a full customer code before proceeding with the sales order.
Upon client acceptance, the quotation transforms into a sales order, marking the official start of the project. This critical document includes:
- Finalized commercial terms from the accepted quote
- Client’s Purchase Order details for reference
- Project-specific identifiers linking to the Project Systems module
- Detailed billing plan, often including milestone-based payments
- Confirmed delivery schedules and logistics information
The sales order serves as the central reference point for all subsequent project activities.
- 💰Down Payment Request: A down payment request is initiated from the sales order. The request is printed and sent to the customer. This request will not create any accounting entries, other than a single line item in Accounts Receivable. The noted item will be cleared once the down payment is received and recorded in Accounts Receivable under a designated special GL Indicator. This process:
- Creates a formal request document based on the agreed terms
- Establishes a receivable entry in the financial system
- Triggers internal processes for procurement and production planning
- Sets up the framework for future milestone billing
The down payment often represents a significant commitment from the client and kickstarts the project’s financial lifecycle.
- 🚚Delivery: As the project progresses through manufacturing stages, the delivery process is closely monitored in SAP. This includes:
- Coordinating with Project Systems to track production milestones
- Generating delivery documentation when products are ready for shipment
- Recording any special handling or shipping instructions
- Capturing proof of delivery for invoicing purposes
Efficient delivery management ensures client satisfaction and timely project progression.
- 📊Billing: The billing plan stipulates that items will be billed only after the completion of all associated contractual obligations and the verification of the corresponding milestone in Project Systems. The billing document information will be automatically populated from the sales document. Billing plan generally includes Down Payment and billable milestones like materials receipt, final inspection and retention with percentages. The billing process is intricately linked to project milestones and deliveries. Key aspects include:
- Automatic triggering of invoices based on confirmed project milestones
- Applying the pre-defined billing plan to ensure accurate and timely invoicing
- Generating comprehensive invoice documents with all relevant project details
- Performance Bank Guarantee, payment receipt with down payment clearing
- Initiating the revenue recognition process in the financial system
Proper billing management is crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow throughout the project lifecycle.
- 📈Revenue Recognition: The final stage involves recognizing revenue in accordance with accounting standards and project progress. This process:
- Utilizes the Results Analysis function to evaluate project status
- Adjusts revenue postings based on the configured recognition method (e.g., percentage of completion)
- Ensures compliance with financial reporting requirements
- Provides insights into project profitability and financial performance
This step is vital for accurate financial reporting and project performance analysis.