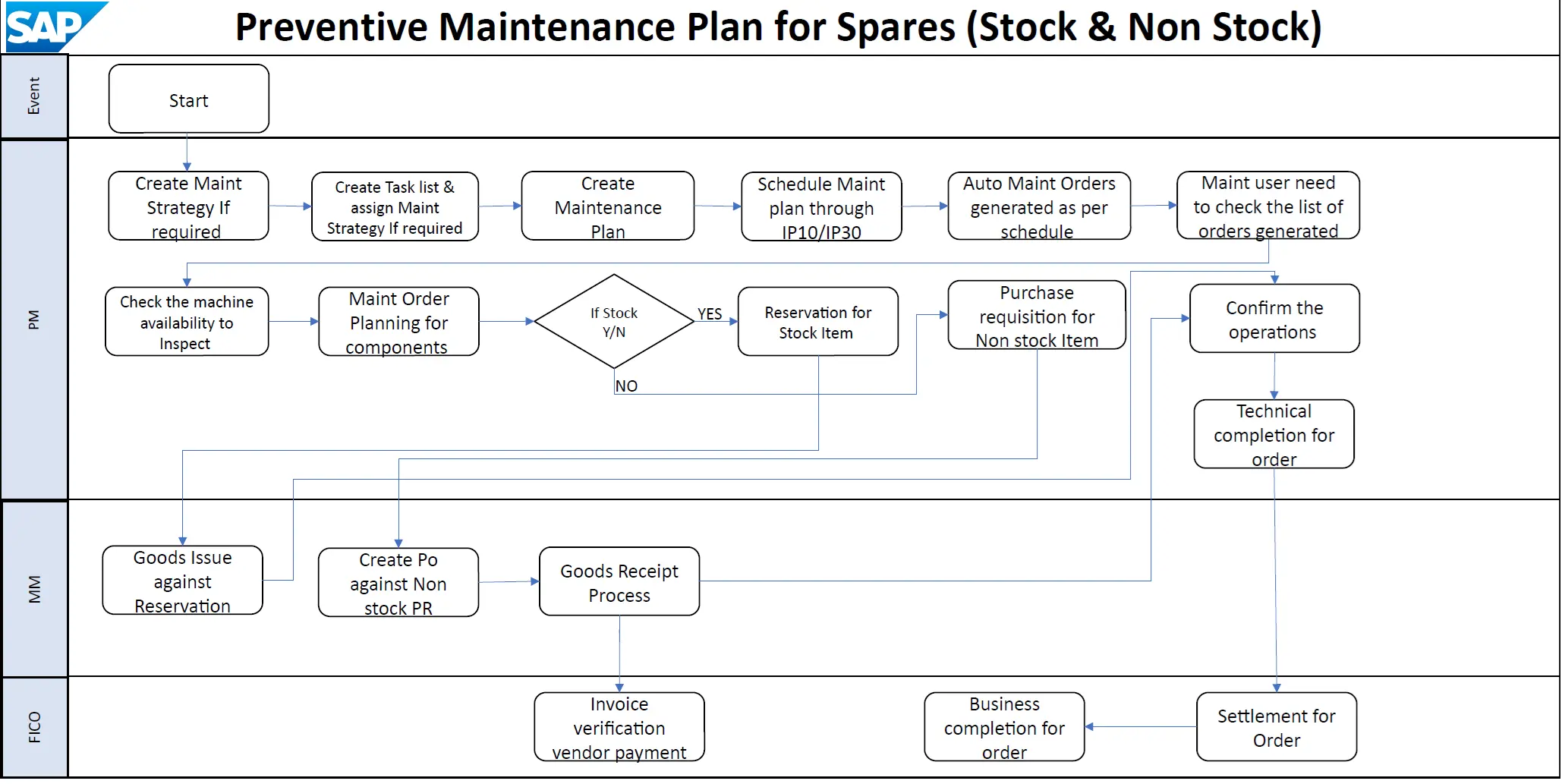
The flowchart illustrates the Preventive Maintenance Plan for Spares (Stock & Non-Stock) within the SAP system, integrating modules such as Plant Maintenance (PM), Materials Management (MM), and Financial Accounting & Controlling (FICO). Below is a detailed breakdown of the process:
🛠️ Plant Maintenance (PM) Activities
- Create Maintenance Strategy If Required (Transaction: IP11): Maintenance strategy allows creating structured plans for maintenance tasks, ensuring that they are performed regularly and systematically. This helps in maintaining equipment reliability and operational efficiency. In this step you will need to select a maintenance strategy that suits the equipment or functional location you are planning for. This strategy determines the frequency and type of maintenance activities.
- Create Task List & Assign Maintenance Strategy If Required (Transaction: IA05 or IA06): Specific maintenance tasks are defined and linked to the strategy. This assignment ensures that the necessary maintenance activities are automatically scheduled and tracked, facilitating easier management of maintenance operations
- Create Maintenance Plan (Transaction: IP41 or IP42): After selecting the strategy, you will enter relevant details such as the description of the maintenance plan. For example, you might specify that it is for an electric motor and include details like energy consumption in kilowatt-hours. The system allows you to define multiple cycles within the strategy, which are referred to as packages.
- Schedule Maintenance Plan through IP10/IP30 (Transaction: IP10 or IP30): Once the maintenance plan is created, you need to schedule it. This involves defining the scheduling parameters, such as the scheduling period and any specific requirements for the maintenance activities. The system will propose dates based on the defined cycles and the current counter readings, allowing for performance-based planning. To ensure that the maintenance plan starts generating work orders, you may need to activate it through additional transaction codes, such as IP10 for scheduling multiple plans
- Maintenance User Needs to Check the List of Orders Generated: After activation, you can monitor the maintenance plan’s performance and make adjustments as necessary. This may involve changing the scheduling parameters or updating the maintenance tasks associated with the plan.
- Check the Machine Availability to Inspect: Suitable maintenance windows are coordinated with production.
- Maintenance Order Planning for Components: The required components for the maintenance order are planned.
- If Stock? (Yes/No): A decision is made whether the required components are in stock:
- If Yes: A reservation for stock item is created (Transaction: MB21).
- If No: A purchase requisition for non-stock item is generated.
- Confirm the Operations (Transaction: IW41): The completion of maintenance operations is confirmed.
- Technical Completion for Order (Transaction: IW32): The maintenance order is marked as technically complete.
📦 Materials Management (MM) Actions
- Goods Issue against Reservation (Transaction: MB1A): Materials are issued from stock based on the reservation.
- Create PO against Non-stock PR (Transaction: ME21N): A purchase order is created for non-stock items based on the purchase requisition.
- Goods Receipt Process (Transaction: MIGO): The receipt of materials is recorded in the system for the purchased non-stock materials.
💰 Finance/Controlling (FICO) Steps
- Invoice Verification Vendor Payment (Transaction: MIRO): Vendor invoices for purchased materials are processed and verified.
- Business Completion for Order: The order is finalized from a business perspective.
- Settlement for Order (Transaction: KO88): Costs associated with the maintenance order are settled.
🔗 Key Integration Points:
- PM to MM: Component requirements trigger goods issue or purchase processes.
- MM to FICO: Material movements and purchases initiate financial transactions.
- PM to FICO: Completed maintenance orders are settled in the controlling module.