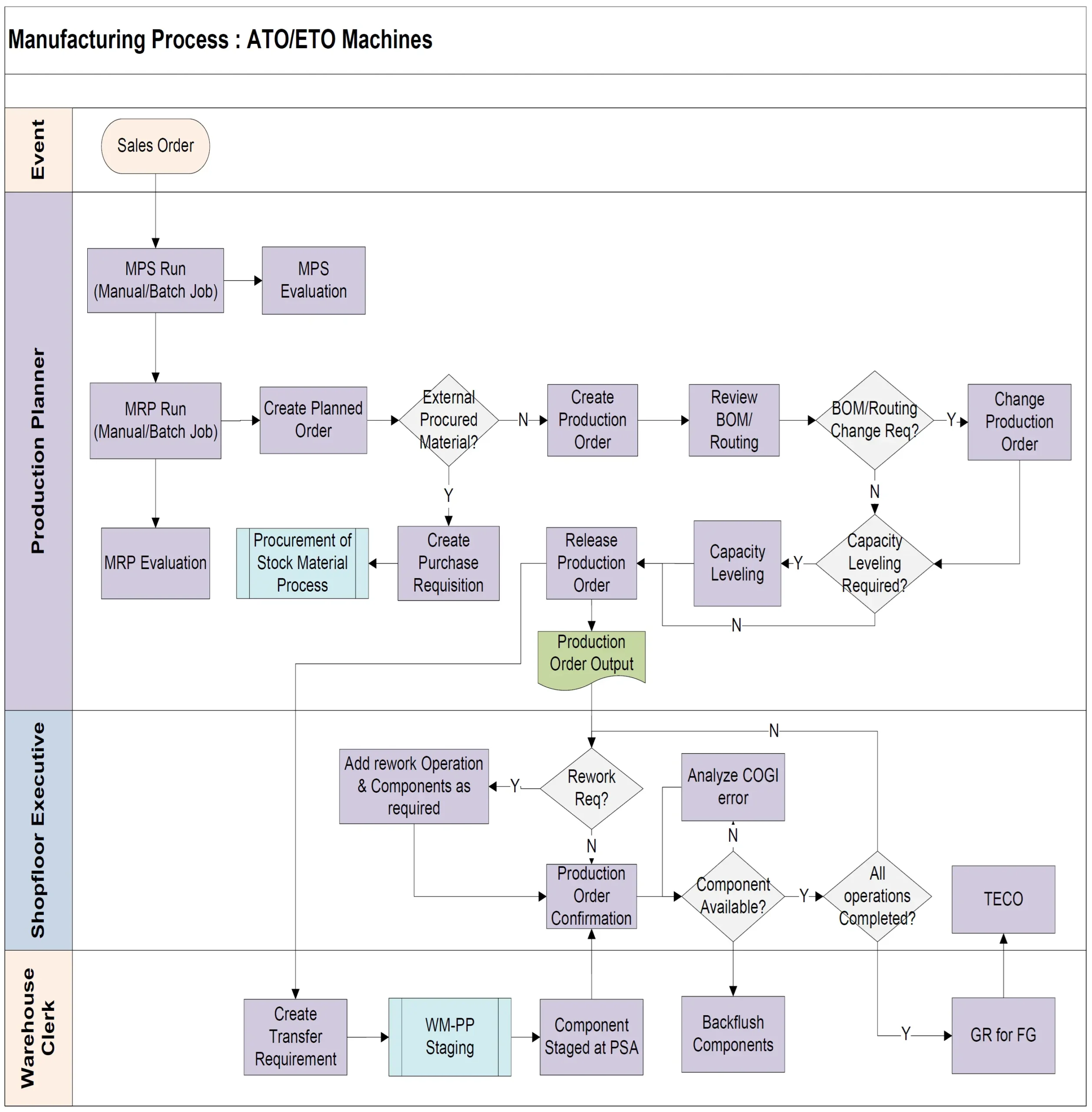
The flowchart illustrates the end to end (E2E) manufacturing process for Assemble-to-Order (ATO) and Engineer-to-Order (ETO) machines in SAP PP. ATO and ETO are production strategies tailored for customized products:
- Assemble-to-Order (ATO): Products are partially assembled from standard components and then customized to specific customer requirements upon order receipt.
- Engineer-to-Order (ETO): Products are designed, engineered, and manufactured entirely based on customer specifications after the order is placed.
These strategies allow for high customization while maintaining some level of standardization. The process in SAP Manufacturing encompasses three main phases as show in diagram:
- Material Requirement Planning (MRP): MRP is a system for calculating the materials and components needed to manufacture a product. In this process:
- An MPS (Master Production Schedule) run is executed, either manually or as a batch job, followed by MPS evaluation.
- An MRP run is then performed, also manually or as a batch job.
- This results in the creation of Planned Orders for in-house production.
- MRP results are evaluated by the Production Planner.
- Procurement and Production Order Creation:
- For externally procured materials, Purchase Requisitions are created and sent to the Procurement of Stock Material process.
- For in-house production, a Production Order is created from the Planned Order.
- The BOM (Bill of Materials) and Routing are reviewed and can be changed if needed.
- Capacity Requirement Planning: This phase ensures that the production facility has sufficient capacity to meet the production plan:
- Capacity Leveling is performed if required to balance workloads across work centers.
- After capacity planning, the Production Order is released and Production Order Output is generated.
- Shop Floor Execution: This is where the actual production takes place:
- Production orders are released to the shop floor.
- Components are staged for production through WM-PP (Warehouse Management – Production Planning) staging.
- The Production Order is confirmed on the shop floor.
- If rework is required, additional operations and components can be added to the order.
- Components are backflushed (automatically issued to the order) during production.
- Any COGI (Confirmation of Goods Issue) errors are analyzed and corrected.
- Once all operations are completed and components are available, Goods Receipt (GR) for the Finished Goods (FG) is performed.
- Order Completion:
- Finally, the order is set to TECO (Technically Completed) status, indicating the production process is finished.
This process integrates material planning, capacity planning, and shop floor execution to manage the production of ATO (Assemble-to-Order) and ETO (Engineer-to-Order) machines efficiently.
Muito bom o fluxo, o documento ficou perfeito